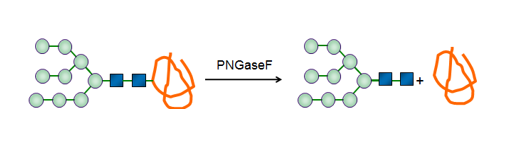
Peptide-N4-(N-acetyl-β-glucosaminyl) asparagineamidase (PNGas eF)
CBGEN00014
Abbr
PNGaseF, Recombinant (Flavobacterium meningosepticum)
Source
E. coli
Species
Flavobacterium meningosepticum
Enzyme Commission Number
3.5.1.52
Molecular Weight
34 KDa
Purity
min 95% by SDS-PAGE
Physical Form
Supplied as a lyophilized powder
Package
100U,250U,500U
Description
A peptide-N4-(N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminyl) asparagine amidase is an enzyme that catalyzes a chemical reaction that cleaves a N4-(acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl) asparagine residue in which the glucosamine residue may be further glycosylated, to yield a (substituted) N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminylamine and a peptide containing an aspartate residue. This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, specifically those acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds other than peptide bonds in linear amides.
Unit Definition
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme that catalyzes the release of 1 nmol N-glycan from RNaseB per minute at 37 °C.
References
1. Active site and oligosaccharide recognition residues of peptide-N4-(N-acetyl-b-D-glucosaminyl)asparagine amidase F. Peter Kuhn et. al. J. Org. Chem. 270 (49), 29493-29497, 1995; 2. Using Secretion to Solve a Solubility Problem: High-Yield Expression in Escherichia coli and Purification of the Bacterial Glycoamidase PNGase F. Trvor Loo et. al. Protein Expression and Purification 24 (1), 90-98, 2002.
